What is AI?
Artificial intelligence or AI alludes to the reenactment of human knowledge in machines that are modified to imitate human-like mental capabilities, for example, learning, critical thinking, discernment, and navigation. Simulated intelligence advancements empower PCs and frameworks to perform undertakings that regularly require human knowledge, going from basic assignments like perceiving designs in information to complex errands like driving independent vehicles or playing vital games
Contribution of scientists in AI
The idea of man-made reasoning (simulated intelligence) has been created and investigated by various specialists, researchers, and masterminds for more than a very long while. While it's hard to credit the idea to a solitary individual, there are a few key figures who have made huge commitments to the field:
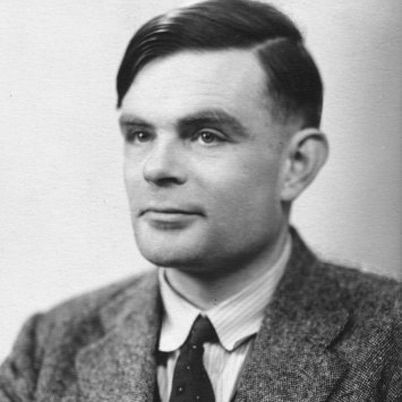
Alan Turing: Frequently thought to be the dad of hypothetical software engineering and man-made reasoning, Alan Turing proposed the possibility of a "general machine" fit for playing out any calculation.
He likewise presented the idea of the Turing Test, a proportion of a machine's capacity to display a wise way of behaving unclear from that of a human.
John McCarthy: Generally viewed as one of the principal architects of simulated intelligence, John McCarthy begat the expression "man-made brainpower" in 1956 and coordinated the Dartmouth Gathering, which is viewed as the introduction of artificial intelligence as a field of study
He made spearheading commitments to computer based intelligence research, including the improvement of the Stutter programming language.
Marvin Minsky: An unmistakable man-made intelligence specialist and mental researcher, Marvin Minsky helped to establish the MIT man-made intelligence Lab and made huge commitments to the investigation of brain organizations, mechanical technology, and human-PC communication.
He proposed the "general public of psyche" hypothesis, which sees the human brain as an assortment of interfacing specialists or subagents.
Herbert Simon and Allen Newell: Herbert Simon and Allen Newell were pioneers in the field of mental brain research and artificial intelligence. They fostered the Rationale Scholar, one of the earliest artificial intelligence programs fit for demonstrating numerical hypotheses.
They additionally presented the idea of "limited levelheadedness," which impacted the plan of simulated intelligence frameworks that copy human critical thinking processes.
Arthur Samuel: A trailblazer in AI, Arthur Samuel fostered the principal self-learning program, known as the Samuel Checkers-playing System, during the 1950s.
This program utilized a procedure called "support learning" to work on its exhibition after some time through experimentation.
These people, alongside numerous others, laid the preparation for the improvement of man-made intelligence as a multidisciplinary field incorporating software engineering, mental science, neuroscience, reasoning, and math. Their thoughts and commitments keep on molding the direction of man-made intelligence
Image
.
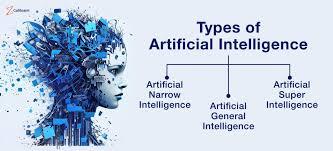
Types Of A.I.
⦁ Narrow AI: This sort of computer based intelligence is planned and prepared for a particular undertaking or set of errands. Models incorporate remote helpers like Siri or Alexa, suggestion calculations on streaming stages, and picture acknowledgment programming.
⦁General AI: General artificial intelligence alludes to man-made consciousness that can comprehend, learn, and apply its knowledge across a large number of undertakings, like human insight. This degree of artificial intelligence is still generally hypothetical and has not yet been accomplished.
⦁Super AI: This is a further significantly developed type of man-made intelligence that outperforms human knowledge in all perspectives. It's simply speculative as of now and brings up issues about the expected ramifications and dangers related to making such a strong knowledge.
Artificial intelligence frameworks can be ordered in light of their functionalities and capacities, for example, AI, regular language handling, PC vision, mechanical technology, and master frameworks. These frameworks depend on calculations and information to simply decide and work on their exhibition over the long run through gaining as a matter of fact.
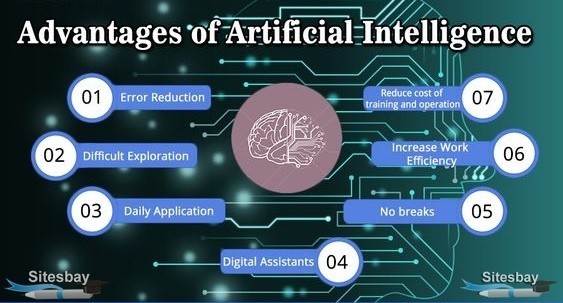
Advantages
⦁Mechanization: simulated intelligence empowers the computerization of tedious errands, prompting expanded proficiency, diminished human blunder, and cost investment funds. This is especially significant in enterprises like assembling, operations, and client care.
⦁ Improved Decision Making: : simulated intelligence frameworks can dissect huge measures of information at high rates, giving important experiences and working with better dynamic cycles. This is useful in fields like money, medical services, and advertising.
⦁ Upgraded Personalization: simulated intelligence calculations can examine client conduct and inclinations to give customized proposals, content, and encounters. This is clear in customized shopping suggestions, content curation via virtual entertainment stages, and versatile learning frameworks.
⦁Prescient Investigation: simulated intelligence fueled prescient examination can conjecture future patterns, results, and ways of behaving in light of authentic information. This capacity is significant in regions like money (anticipating market patterns), medical services (foreseeing illness flare-ups), and support (prescient upkeep in assembling).
⦁ Effective Asset Usage: computer-based intelligence can improve asset distribution by anticipating requests, advancing courses, and overseeing stock levels. This prompts decreased squandering and further developed asset productivity in ventures, for example, transportation, store network executives, and energy.
⦁24/7 Availability: artificial intelligence-controlled menial helpers and chatbots can give nonstop client care and help, further developing availability and upgrading client experience.
⦁ Clinical Headways: simulated intelligence is altering medical care with applications like clinical picture investigation, drug disclosure, customized medication, and far-off quiet checking. Artificial intelligence-driven demonstrative apparatuses can further develop exactness and effectiveness in illness location and treatment arranging.
⦁Imaginative Arrangements: simulated intelligence encourages advancement by empowering the improvement of novel items, administrations, and arrangements. This remembers headways for fields like independent vehicles, savvy home innovation, computer-generated reality, and mechanical technology.
⦁Wellbeing and Security: artificial intelligence controlled frameworks can upgrade security and security through applications like facial acknowledgment, extortion recognition, online protection, and reconnaissance. These advances help forestall and alleviate gambles in different areas.
⦁Ecological Effect: simulated intelligence adds to natural supportability through applications like accuracy farming, energy enhancement, squander the board, and environmental displaying. These innovations assist with tending to ecological difficulties and advance maintainable practices.
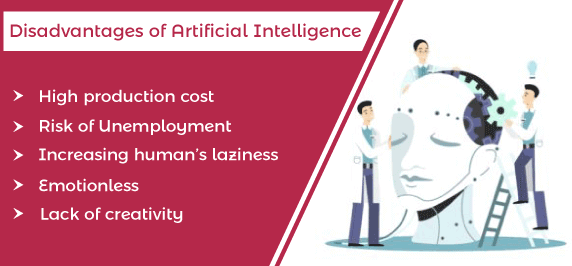
Disadvantages:
While man-made brainpower (artificial intelligence) offers various advantages, it additionally presents a few detriments and difficulties
⦁Work Relocation: Robotization driven by computer based intelligence innovations can prompt work dislodging as undertakings recently performed by people are mechanized. This can bring about joblessness, especially for people in low-talented or schedule-based positions.
⦁Predisposition and Separation: man-made intelligence calculations can unintentionally propagate inclinations present in the information used to prepare them, prompting oppressive results. This can bring about uncalled-for treatment or choices in regions, for example, employing, loaning, and law enforcement .
⦁Protection Concerns: artificial intelligence frameworks frequently depend on huge datasets containing touchy data, raising worries about information security and security. Unapproved access or abuse of this information can bring about security breaks and data fraud.
⦁ Moral Predicaments: man-made intelligence raises complex moral quandaries, like the utilization of independent weapons, intrusion of protection through reconnaissance advancements, and the effect on human independence and poise.
⦁Dependence on Information Quality: The exhibition of computer based intelligence frameworks vigorously relies upon the quality and representativeness of the information used to prepare them. One-sided or deficient information can prompt wrong or questionable results.
⦁Absence of Straightforwardness: Some simulated intelligence calculations, especially profound learning models, work as "secret elements," making it challenging to comprehend how they show up at their choices. The absence of straightforwardness can sabotage trust and responsibility in computer based intelligence frameworks.
⦁ Network safety Dangers: artificial intelligence controlled frameworks are helpless against cyberattacks, including ill-disposed assaults intended to control or hoodwink simulated intelligence calculations. Getting simulated intelligence frameworks against such goes-after is a huge test.
⦁Reliance and Overreliance: Overreliance on simulated intelligence frameworks without human oversight or intercession can prompt carelessness and a deficiency of basic abilities. Human judgment and mastery are as yet important to decipher simulated intelligence-created experiences and pursue informed choices.
⦁Monetary Disparity: The advantages of computer-based intelligence may not be uniformly appropriated, prompting extending financial imbalance between the individuals who approach computer-based intelligence innovations and the people who don't. This can compound existing aberrations in riches and opportunity.
⦁Joblessness and Reskilling: artificial intelligence driven robotization might disturb conventional ventures and occupations, expecting laborers to secure new abilities or go through reskilling projects to stay employable. Notwithstanding, admittance to quality instruction and preparing valuable open doors might be restricted for certain people.
Tags
AI World